Bolt pretightening force is an important factor affecting sealing. The pre-tightening force must compress the gasket to achieve the purpose of the initial seal. Properly increasing the bolt pre-tightening force can increase the sealing ability of the gasket, because increasing the pre-tightening force can make the gasket retain a greater contact surface specific pressure under normal working conditions. However, the pre-tightening force should not be too great. Otherwise, the gasket will yield as a whole and lose its resilience, or even extrude or crush the gasket. In addition, the pretightening force should be applied to the gasket as evenly as possible. Measures such as reducing the bolt diameter, increasing the amount of bolts and adopting appropriate pre-tightening methods are usually taken to improve the sealing performance.
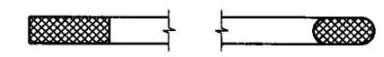
(a) Non metallic gaskets (b) Metal clad gaskets
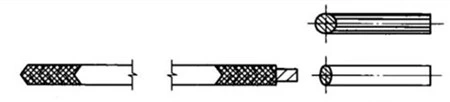
(c) Spiral wound gaskets without locating rings (d) Spiral wound gaskets with locating rings (e)Metal gaskets
Gasket performance
A gasket is an important component of sealing, the main types are shown in the following figures:
The function of the gasket is to seal the gap between the sealing surfaces of the two flanges and prevent fluid leakage. Gaskets include non metal gaskets, combinations of non metal and metal gaskets and metal gaskets. Appropriate gasket materials require that the gasket can produce the necessary elastic deformation without being crushed or squeezed out under the action of appropriate pre-tightening force. At the same time, the distance between the flange sealing surface is increased during operation, and the gasket material should has sufficient resilience to keep the gasket surface in close contact with the flange surface, continually maintaining good sealing performance. The working medium and working temperature should also be considered when selecting gasket materials. The width of the gasket is also an important factor affecting the seal. The wider the gasket is, the greater the pre-tightening force and the size of bolts and flanges require.
①Nonmetallic gaskets such as rubber, asbestos rubber and polytetrafluoroethylene gaskets are commonly used on medium and low pressure equipment and pipeline flanges. They have good corrosion resistance and flexibility, but their strength and temperature resistance are poor. They are usually cut from the entire gasket sheet. The shape of the entire gasket is a ring with a rectangular cross section.
②In order to improve the strength and heat resistance of the gasket, thin steel belts and asbestos belts (PTFE belts or flexible graphite belts) are winded together to form spiral wound gaskets, or asbestos or other nonmetallic materials are wrapped with metal sheets to form metal clad gaskets, which have multiple sealing effects and good resilience. They are used in higher temperature and pressure ranges and can maintain good sealing under pressure and temperature fluctuations, which are widely used. Spiral wound gaskets are made by winding steel belts with asbestos, polytetrafluoroethylene, flexible graphite or other filling belts. Weld the beginning and end of the metal strip to prevent looseness. In order to increase the elasticity and resilience of the gasket, both the metal strip and the nonmetal strip are made into a wave shape. There are two wave shapes, namely the V shape and the W shape. The figure below is the V shape and there are four structural types in total.
Spiral wound gaskets
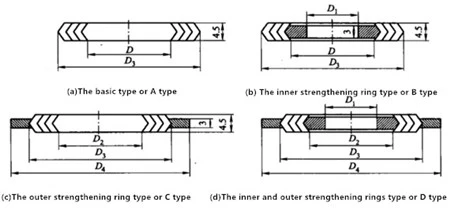
Type A without the strengthening ring is also known as the basic type and is used for tongue-and-groove sealing surfaces.
Type B with the inner strengthening ring is used for concave and convex sealing surfaces.
Type C with the outer strengthening ring is used for flat sealing surfaces.
Type D with inner and outer strengthening rings are used for flat sealing surfaces.
③The metal clad gasket is made of asbestos rubber sheet as the inner core, and the outer part is a thin metal plate with a thickness of 0.2 to 0.5mm. See the following figure:
The metal clad gasket
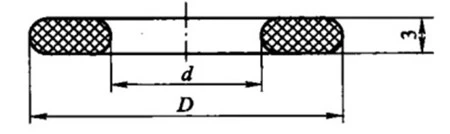
The material of the metal sheet can be aluminum, steel and its alloys, stainless steel or carbon steel with good quality. Metal clad gaskets are only used for B Type socket welded flanges and welding neck flanges.
④Metal gaskets are commonly used for flanges of high-pressure equipment and pipelines. The materials include soft aluminum, copper, mild steel and stainless steel. In addition to metal gaskets with rectangular cross-sections, there are also metal gaskets with elliptical or octagonal cross-sections and other special shapes. When the operating pressure is very high; the leakage rate is very strict; the temperature is very high or the corrosiveness is very strong. Metal gaskets can be used. The specific pressure value of the metal gasket is very large. In order to reduce the bolt force, the pressing surface must be very narrow. There must be a small surface roughness, relying on the extremely narrow pressing surface to maintain a good seal. Ra is smaller than or equal to 2.5μm or being smaller than or equal to 0.63μm.