The maximum working pressure of most process pressure pipelines on offshore platforms can reach 10MPa, and that of some pipelines can reach 20MPa, which makes the pipelines bear great stress. Under the influence of marine environmental factors, it is easy to cause defects or crack expansion of pipes until breaking occurs. Through magnetic particle, infiltration, ultrasonic and other technical methods, it is found that there were environmental cracking type cracks in offshore platform pipelines, and two serious cracks are analyzed in detail.
1.3.2.1 Hot cracks on duplex steels
A crack was found on the welding seam of a condensate dual-phase steel pipe (Figure 6). After testing the material of the welding seam, it was found that the hardness value and ferrite content of the welding seam crack area were significantly lower than the normal values. The ferrite content is close to 2.7% of austenitic stainless steel. The ferrite content of normal duplex steel is between 35% and 50%. The working pressure of this pipeline is 3.4 to 11.7MPa, and the working temperature is 14.7 to 40°C. The cracks were found on the outer surface of the welding seam, which can rule out the possibility of decarburization and deterioration of materials. After metallographic inspection, it was found that there was more bifurcation at the crack end of the pipeline and had the morphological characteristics of hot cracks. Therefore, it is preliminarily judged that the formation of the crack is due to the misuse of the austenitic stainless steel electrode. In the long-term service process, the pipeline pressure is cyclically adjusted with the requirements of the production in different periods, and the strength of the austenitic stainless steel electrode was significantly lower than that of the dual-phase steel. Various factors cause the crack to expand to the weld seam surface.

Figure 6 The macroscopic morphology of hot cracks in dual-phase steel
Therefore, for such cases of cracks caused by misuse of austenitic stainless steel electrodes, the ferrite content detection of the duplex steel welding seam should be strengthened (4 directions in the whole circle), and the welding part with abnormal ferrite content should be found in time. Carry out metallographic analyses, while conducting more penetration testing. When the crack was ultrasonically inspected, no obvious defect echo signal was found. However, during repair, it was found that the depth of the crack reached 6mm. This was caused by the metallographic structure of austenitic stainless steel being larger than that of ferritic stainless steel, and it is easy to form a transmission layer at the joint surface of the two materials. Even if the sound wave can penetrate effectively, the reflection echo may not be received. Therefore, it should be noted that ultrasonic testing has certain limitations for detecting such special cases, and such abnormal conditions need to be screened in the detection process.
1.3.2.2 Cold cracks on carbon steel pipes
A crack with a length of about 40mm and a height of 7mm was found on a natural gas pipeline (Figure 7). The crack shape mainly extends vertically downward along the weld toe, while extending circumferentially along the weld toe and expanding to the welding at the end of the crack. No fusion was found in the process of eliminating the crack, and the crack was vertically downward on the weld toe in the welding process. According to the analysis, the reason for the formation of the crack is that there is a hardened structure in the welded joint in the welding process, which embrittles the material properties. At the same time, diffusible hydrogen generated during welding does not diffuse effectively during cooling and accumulates at the welding defect part, resulting in increasing in partial hydrogen partial pressure. In addition, the pipe fittings and pipes are limited during welding, and the deformation caused by the temperature difference in the cooling process is limited, resulting in restraint stress. Welded joints contain defective hardened structures that crack under the influence of hydrogen partial pressure and restraint stress. Under normal circumstances, the hydrogen partial pressure is released after the crack is formed, and the crack does not have the conditions for expansion without external force. The crack propagation is because the pipeline has a high working pressure of 7.9 to 11.28MPa. The pipeline is subjected to great stress, which continuously expands along the circumferential direction of the welding seam.
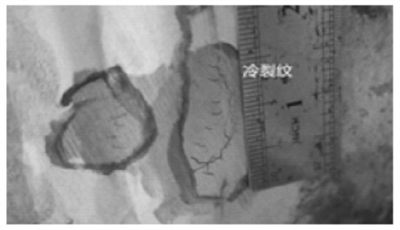
Figure 7 The macroscopic morphology of cold cracks of carbon steel
1.3.3 Other damage
Other damage on offshore platforms mainly involves the following aspects: bending of pipelines, failures of flange sealing surfaces, failures of pipelines due to fatigue loads such as wind loads for a long time, and damage or deformation of material surfaces caused by external forces on pipe fittings.
The bending of the pipeline is mainly caused by the falling off or fracture of part of the support frame due to corrosion. The fracture of the support frame (the fracture of the pipeline or valve support frame) will affect the distribution of the pipeline force due to the large volume and heavy weights of the high-pressure pipeline control valve of the platform, and in severe cases, it will cause bending of the entire pipeline and even induce cracks in the weld joint. A crack happened at the welding joint near the valve of a platform in the South China Sea due to the unreasonable distribution of the support frame, the material of the welding joint near the valve not meeting the standard and other factors. The macro inspection of the pipeline support frame should be strengthened, and the surface inspection should be provided if necessary. The regular inspection of the front and rear flange welding seams of the control valve and the welding seam of the adjacent pipe fittings should be strengthened, and the corrosion of the support frame should be checked. If there is any fracture, replace it in time.
Strict requirements of tightness were put forward for the high-pressure working characteristics of process pipelines and equipment of offshore platforms. When the equipment operates under complex conditions for a long time, there will be few leakages for the flange sealing surface. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the detection of the flange sealing surface, check the abnormal parts in time, and do a good job of isolation and protection so as to facilitate the maintenance plan before the production is stopped. For the detection of such flange sealing surfaces, the focus should be on the positions of various valves, equipment flange connections and instrument connections. Leak detection methods include foam, combustible gas alarm, professional VOC detection, etc.
In addition to the above-mentioned damage, there are more common cases of deformation or damage to material surfaces caused by an object striking offshore platforms. Such situations are mainly caused by impacting equipment in the daily production process.